Filter, Channel, and System#
Lowpass Equivalent of a Bandpass System#
Bandpass Systems#
A bandpass system is a system whose transfer function is centered around a frequency \(f_0\) and its mirror image at \(-f_0\).
Definition: Lowpass Equivalent of System Impulse Response
A bandpass system is characterized by an impulse response \(h(t)\), which is itself a bandpass signal.
The lowpass equivalent of \(h(t)\), denoted by \(h_l(t)\), is defined as:
Input-Output Relationship in Bandpass Systems#
When a bandpass signal \(x(t)\) passes through a bandpass system with impulse response \(h(t)\), the output \(y(t)\) is also a bandpass signal. The relationship between the spectra of the input and output is:
Lowpass Equivalent Relationship#
For the lowpass equivalents of the signals and system, the relationship is given by:
Expanding this:
Simplifying further:
Time Domain Relation#
In the time domain, the relation between the input \(x(t)\), the system impulse response \(h(t)\), and the output \(y(t)\) is:
where \(\circledast\) denotes the convolution.
Key Insight
When a bandpass signal passes through a bandpass system, the relationship between their lowpass equivalents is analogous to that between the bandpass signals.
The only difference is the introduction of a scaling factor of \(\frac{1}{2}\) for the lowpass equivalents.
Matlab Example: Lowpass Filtering of Tones#
Reference: Lowpass Filtering of Tones
This example demonstrates how to generate, process, and analyze a signal with specific frequency components and noise, and how a lowpass filter isolates desired frequencies:
Signal Generation:
A signal is created with a duration of 1 second, sampled at a rate of 1 kHz (1000 samples per second). This means the signal will have 1000 samples for the 1-second duration.
The signal consists of two sinusoidal tones:
A low-frequency tone at 100 Hz.
A high-frequency tone at 300 Hz.
Amplitude adjustment: The amplitude of the 300 Hz tone is set to twice that of the 100 Hz tone, making it more prominent in the signal.
Noise addition: Gaussian white noise with a variance of \( \frac{1}{100} \) is added to simulate a realistic noisy environment. White noise introduces random variations across all frequencies.
Lowpass Filtering:
A lowpass filter is applied to the signal. This filter is designed to pass frequencies below a certain threshold and attenuate higher frequencies.
The threshold (passband frequency) is set to 200 Hz, meaning:
The low-frequency component at 100 Hz is retained.
The high-frequency component at 300 Hz is attenuated or removed, along with any noise above 200 Hz.
Matlab Simulation#
% Sampling frequency (1 kHz)
fs = 1e3;
% Time vector (1 second duration, sampled at 1 kHz)
t = 0:1/fs:1;
% Generate the signal:
% - Two sinusoidal tones: 100 Hz and 300 Hz
% - Amplitudes are 1 and 2, respectively
% - Add Gaussian white noise with variance 1/100
x = [1 2]*sin(2*pi*[100 300]'.*t) + randn(size(t))/10;
% Apply a lowpass filter:
% - Passband frequency: 200 Hz
% - Sampling frequency: fs (1 kHz)
filtered_x = lowpass(x, 200, fs);
% Plot time-domain and frequency-domain views
Visualization:
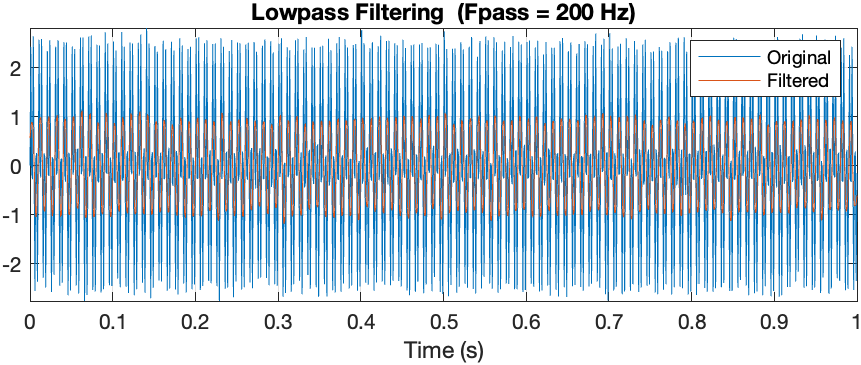
The original signal is displayed in the time domain, showing the combined tones and noise.
The filtered signal is displayed to show how the high-frequency tone and noise are reduced, leaving mostly the 100 Hz tone.
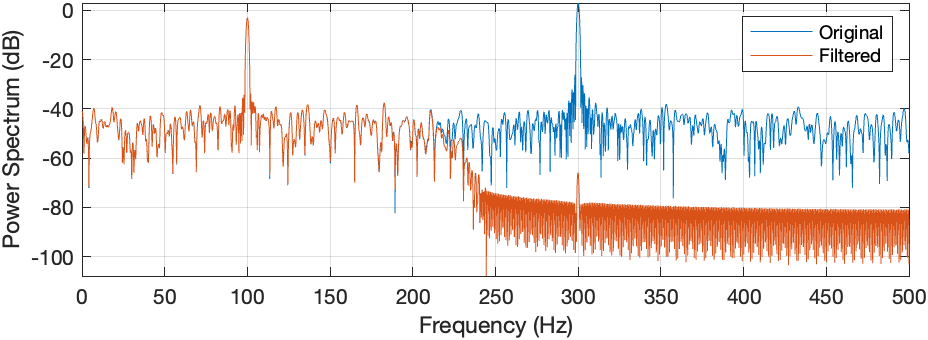
Spectra (frequency-domain representations) of both signals are plotted:
The spectrum of the original signal shows two peaks at 100 Hz and 300 Hz, corresponding to the tones, along with the noise spread across all frequencies.
The spectrum of the filtered signal shows only the peak at 100 Hz, as the 300 Hz tone and higher-frequency noise are removed by the filter.